
Git & GitHub for Beginners
Git is a distributed version control system that allows developers to track changes made to their code over time. With Git, developers can create snapshots of their code called commits and keep track of multiple versions of their codebase.
Bijoy Kar
February 24, 2023
Hi, everyone I am Bijoy Kar. Thank you for reading Git & GitHub for Beginners. Thank you to all of you for supporting me. I am quite active, I post daily on Twitter and LinkedIn so if you like then give me a follow.
What is Git ?
Git is a distributed version control system used for software development and other types of version control. It was created by Linus Torvalds in 2005 to manage the development of the Linux kernel.
Git allows multiple developers to work on the same codebase simultaneously and keep track of changes made to the code. It allows developers to make changes to their local copy of the code and then commit those changes to a central repository, which can be accessed by other developers.
Git is widely used in the software development industry because it makes it easy to collaborate with others, maintain multiple versions of a codebase, and track changes over time. It is also flexible and can be used with a variety of workflows and project structures.
Git Installation
To install git visit https://git-scm.com/downloads . Download git according to your operating system. In the setup wizard leave everything default.
Git Installation with Git
Visit https://github.com/git/git and clone the repository and follow the installation guide
git clone https://github.com/git/git
Get Started with Git
Basic Workflow of Git
- To work with Git we need to initialize a directory as a git repository, means we need to tell git to make that folder / directory a git repository. To do so use this command
git initAfter the git initialization a .git directory will be created in the directory which is hidden. Here all the changes and commits data are stored.
- Now we add some files to understand the workflow of git. We make a
pythonfile for example
def add(a,b):
return a+b- Now we are going to check the status of the local repository
git status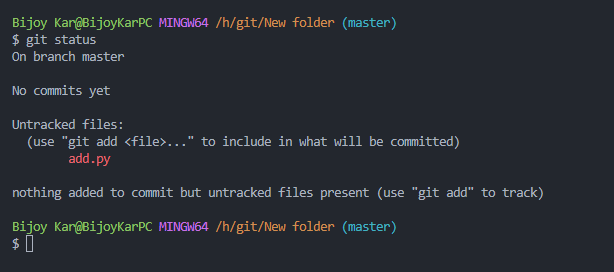
- The
add.pyis untracked, to track the changes of the file we will stage the file.
git add add.pygit add add.py this command will stage only the add.py file.
git add .git add . this command will stage all the new files or changed files in the local repository.
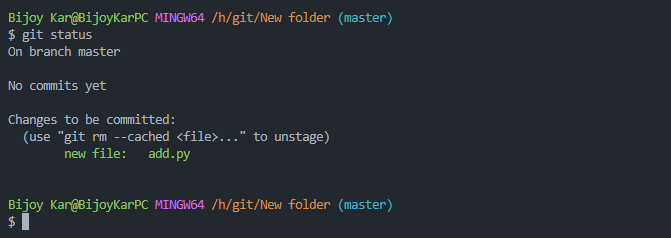 Now the file is staged. The green colored file name indicate that it is tracked.
Now the file is staged. The green colored file name indicate that it is tracked.
- After staging the file now it is time to make a commit means making a checkpoint of the codebase. In future if we make a mistake or need this codebase then we can return here.
git commit -m"initial commit"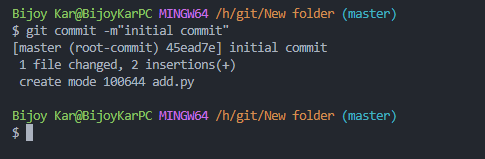
Every commit need a commit message here the message is “initial commit”. By the message we determine what changes are made in that commit. It is must to provide a commit message. By convention we give the message of first commit “initial commit”.
We are assuming that you have already a GitHub account and you can make a remote repository
- Add the remote repository to your local directory
git remote add origin <url of your remote repo>Here origin is the name of remote repo, by convention we give the remote repo a name of origin
- We make sure to
pullbeforepushchanges into remote repo
git pull origin masterThe format is git pull <remote repo name> <branch name>
- By
pushwe push our local changes or commits into remote repo
git push origin masterThe format is git push <remote repo name> <branch name>
Thank you for reading this article, if like to read more of my article then subscribe my newsletter Weekly Coding Dose and give a follow. I post daily on LinkedIn and Twitter.